Healthcare is a wider term. In addition to hospitals, the Healthcare industry comprises of related products
and services such as medical devices,
clinical trials, outsourcing, telemedicine, medical tourism, health insurance,
and medical equipment. The industry is growing at a tremendous pace owing
to its strengthening coverage, services and increasing expenditure by public as
well as private players.
Several existing and emerging
technologies will have a positive impact on the healthcare industry in the
future. Artificial intelligence, machine learning, virtual
reality and others will become critical tools for healthcare providers
and organizations to perform more efficiently.
With the evolution of new techniques, using advanced technologies and spending on research, healthcare is no more a system of patient care only.
Earlier hospitals were more focused on managing revenues rather than cost. The
yardstick of operational efficiency was bed occupancy. But in modern scenario, with the emerging insurance sector and competitive pricing has kept a control
over the revenue side whereas modern technique of treatment has shifted the
focus away from bed occupancy.
The healthcare industry is left far behind other industries in adopting cost management systems
because of the characteristics of the
hospital industry like quantum of services rendered along with the complexities
involved in each service, cross department services, the permutations and
combinations of services provided to a patient, changing technologies and hence
the obsolescence of the medical equipment which makes it difficult
to arrive at the cost of resource as well as service.
Hospitals have various specialties/ medical departments
and each specialty provides different types of services.
The type of services and number
of services provided to a patient again depends on the patient diagnosis and
clinical complications. The process involved, cost of resources and material
may vary from patient to patient for the same procedure.
For example, for the two patients
having angioplasty, the cost may differ based on the clinical complications -
type of stunt used, number of stunts planted, procedure done by very
experienced and skilled doctor or by a doctor having less experience- based on
the complexity of the angioplasty procedure done for a particular patient.
Nowadays, due to the changes in the insurance benefits, the patients are comparing hospital prices which is putting pressure on the hospitals to set the prices at levels that reflect the costs of providing care. If these changes materialize, cost accounting information will become a much more important part of hospital management than it has been in the past.
What is Cost Management
Cost Management is the process of
managing and controlling monetary resources while running a business. It is
also defined as the process of planning and controlling the budget of a business.
Having a good cost management system helps the organization to estimate and
allocate its budget and thus reduces the budget overruns with accurate
forecasting of the expenditure. It also ensures having effective cost control
measures.
The objective of the cost management process is not only to reduce costs but to reduce costs only to that extent
where the quality of the product or
service is not hampered.
Healthcare organizations that
carefully and strategically reduce spending can avoid negatively impact their
ability to deliver an excellent patient experience.
Resource allocation, cost estimation, cost budgeting and cost control are the major functions of the cost management process.
Cost Management Process
· Evaluate hospital- and department-specific data.
· Determine optimal resource allocation to achieve quality and cost goals.
· Develop a strategic management action plan for change and process improvement.
· Provide routine concise feedback on goal attainment, which leads to sustainability.
Cost Management accounting methods
1. Activity
Based Costing
Activity based
costing takes a rational approach to product and service costing, since it
begins with an effort to identify the fundamental activities and resources
involved in producing an output. The indirect expenses are then allocated to
the activities using cost drivers that are carefully selected to reflect the
use of each particular resource pool. This methodology has been found to
produce accurate and rational financial management information, and to provide
information that helps managers make accurate product mix decisions, product
price calculations, and consumer profitability analysis.
However, ABC is
not without its drawbacks. Identifying the appropriate cost drivers, an
essential step in the ABC process, requires significant managerial time and
financial investment. Moreover, significant investments are required to
maintain an ABC system as the organization’s processes change
2. Performance-focussed
Activity Based Costing (PFABC)
PFABC is an
intensive costing process that requires several steps to properly allocate
indirect expenses. PFABC is similar to ABC in that it requires the
identification of major cost activities. With PFABC, the actual resources for
each activity can be assessed in a variety of ways, including interviews,
surveys, or based on actual utilization of time, materials or other resources.
The extra processes in the PFABC approach make PFABC more difficult to
establish but enable PFABC to offer a richer and more detailed examination of
the organization’s activities. It is a powerful planning and performance
evaluation tool, as it can identify variances, such as rate, efficiency, and
volume variances. It is the one costing mechanism that is used to examine the
efficiency and effectiveness of an organization.
3. Ratio
of Cost to Charges (RCC)
RCC is a costing
method specific to the health care industry. Hospitals uses traditional costing
methods to allocate overhead costs to clinical departments and thereby estimate
the full cost of each revenue-producing department. These estimates are paired with
information about the total charges for all services provided by a clinical
department to compute a department-level ratio of cost to charges (RCC). The
RCC, when multiplied by the hospital’s charge for a specific service, can be
used to estimate the cost of providing an individual. Service cost estimates
made using this method are of questionable accuracy.
4. Relative
Value Units (RVUs)
RVU is an approach to weigh the intensity of the each healthcare service (CDM). The approach uses the weights defined in RVU for Physicians and for the Hospital. RVUs define the value of a service or procedure relative to all services and procedures. This measure of value is based on the extent of physician work, clinical and nonclinical resources, and expertise required to deliver the healthcare service to patients.
Comparison of costing methods used in healthcare sector
Other cost management techniques suggested are Target Costing, Benchmarking and Balanced scorecard.
Supply Chain management in Healthcare Industry
Healthcare supply chain management is a collection of processes, teams, and the transportation of medicines and other supplies, medical tools, medical equipment and other products required by healthcare professionals to execute their jobs.
- Reduce operational costs with better processes and automation: Efficient logistics enable medical enterprises to compete more effectively in the marketplace. Helps in managing pricing fluctuations, reducing the negative impact when deliveries are delayed or avoiding unanticipated shortages and better inventory controls.
- Gives a competitive advantage
- Improve the three C’s: communication, collaboration, and coordination between vendors, suppliers, transportation firms, and shipping organizations
- Increased transparency: Logistics partners should improve transparency by coordinating live tracking updates and establishing open communication channels to increase customer service.
- Aids in demand forecasting : Using healthcare supply chain analytics to estimate demand correctly, improve stock planning and management, and respond more quickly to changing market conditions by combining supply chain and clinical data.
1.
Outsourcing
and Standardizing Service Contracts
·
Food /Canteen Service Contracts
·
Clinical Engineering contracts
·
Environmental service contracts
Outsourcing and
standardizing services through a single vendor wherever possible to lower
operating costs and also boost patient satisfaction.
2.
Examining
Patient Flow
Creating a
standardized way for how patients move around within a hospital can reduce
costs and improve the quality of care these patients receive. Optimizing
patient flow helps to:
·
Decrease delays and wait times
·
Improve room turnaround times
·
Ensure maximum occupancy for every hospital
bed
This reduces the
bottlenecks, helps the patient flow moving and thus reducing the overall costs
while bolstering the patient satisfaction
3.
Healthcare
staff
Cost management
in healthcare does not mean reducing the head count.
It means
· retaining skilled and efficient staff and
thereby reducing employee turnover, retaining great associate and consultant
doctors
·
conducting staff training and development
workshops
·
recognizing and providing incentives for good
performance
·
optimize scheduling
which contributes
to long term cost reduction.
4.
Preventing
re-admission
CONCLUSION
Challenges faced by the health
care sector are the complexities due to huge number of services, various
specialities, inter-dependencies, other ancillary profit centers, lack of
accurate data, identifying the activities and its related data.
The solution is to implement a
good cloud based integrated ERP with inventory management, fixed assets, cost
management and business intelligence modules along with the operations and
finance/accounting, HR modules. More focus to be given on outcome-based reporting and evaluation to be done monthly/ quarterly to take necessary action.
Even if the costing management systems have been implemented in the hospitals, the accounting experts say that “…there is an almost complete lack of understanding of how much it costs to deliver patient care…Instead of focusing on the costs of treating individual patients with specific medical conditions over their full cycle of care, providers aggregate and analyze costs at the specialty or service department level.”
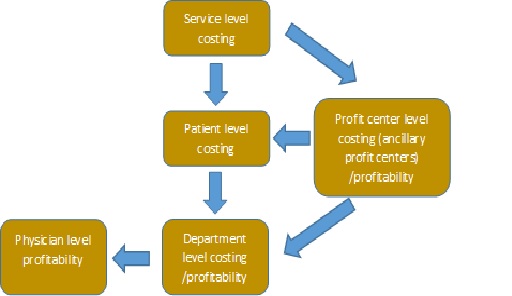
Adherence to Companies (Cost Records and Audit) Rules, 2014 & Amendment thereto and maintenance of cost records as prescribed in Form CRA 1 of the Rules to the extent applicable will enable the healthcare service provider to arrive at costs at different levels including patient level and use it for further analysis.
COST RECORDS AND COST
AUDIT
Any company engaged in “Health services, namely functioning as or
running hospitals, diagnostic centers, clinical centers or test laboratories”
are required to maintain cost records
and having an overall turnover from all
its products and services or Rupees Thirty-Five crores or more during the immediately preceding
financial year needs to maintain prescribed cost records in accordance with
Form CRA 1 of the Rules to the extent applicable. A company need to get cost records audited in
accordance with these rules if the overall
annual turnover of the company from all its products and services during
the immediately preceding financial year is Rupees
100 crore or more.
Customized Cost sheets (different levels) and Cost MIS reports/ Dashboard provided during the implementation of the cost management system.
CMA Manjula Gutti
Cost and Management Accountant
Email id: manjula_asso.cma@rediffmail.com
Mobile No: +91 9989065215
·